
Suspensory ligament : it attaches the ciliary body to the lens and keeps the lens in position Its contains tissues blood vessels and ciliary musclesĬiliary muscles : It consist of sheets of smooth muscles fibers forming bundles of circular and radial muscles which when they contract or relax alter the shape of the lens during accommodation It equally prevents internal reflection of light the eye.Ĭiliary body : It is the junction of sclera and cornea. It is covered with pigmented cells which absorb light and shield the retinal. They also protect the retinal from bright light by reflex actionĬhoroid: it is the middle layer of the eye, rich in blood vessels which supply the retinal and other parts with food and oxygen. Įyelids: They protects the cornea from mechanical and chemical damage. its the window of the eye and lets light in the eye.Ĭonjunctiva : It is a thin transparent layer of cells protecting the cornea and is continuous with the epithelium of eyelids. It has a curved which helps in refracting light towards the retinal. Ĭornea: It is transparent front part of the sclera. It protects and maintains the shape of the eye ball. Scalera : It is the external layer of the eye which is white, very tough and contains collagen fibers.
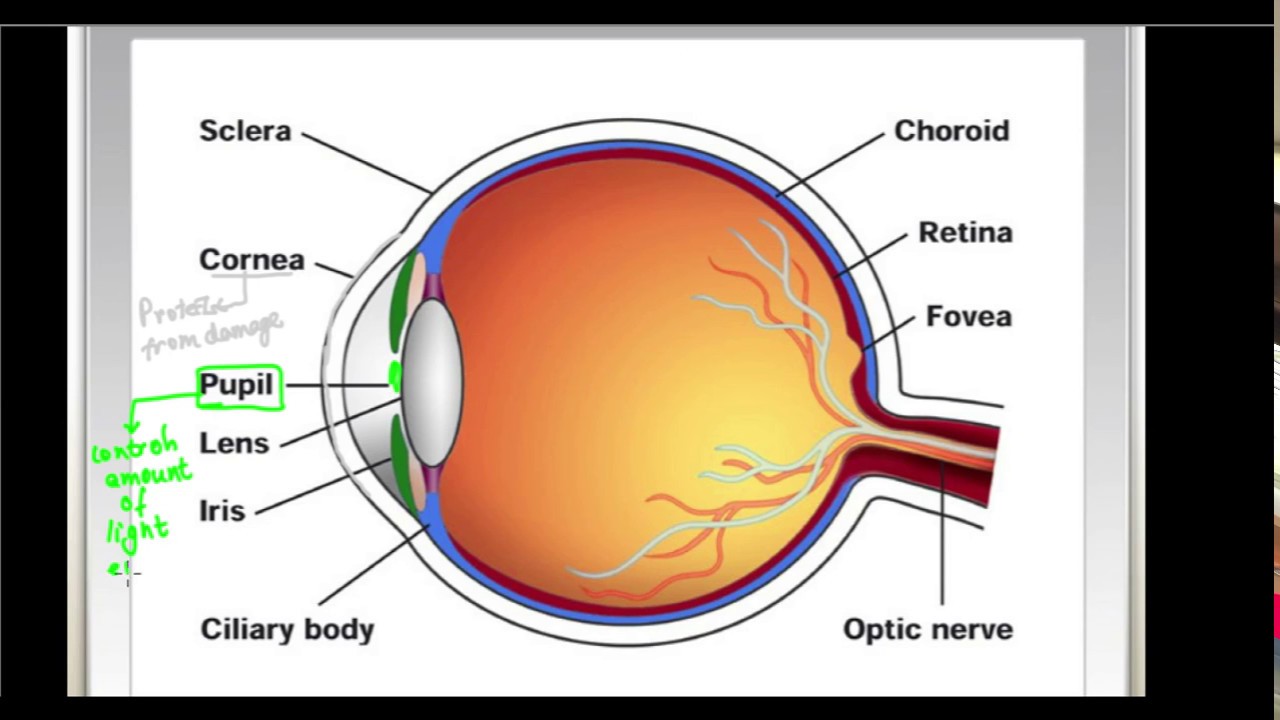
A cross section of the eye shows three concentric layers The sclera, the choroid and the retina. Most of the eye is composed of accessory structures concerned with bringing the visual field to the photo receptor cells in the retina. The eyes are held in protective bony socket of the skull called orbits by four rectus muscles and two oblique muscles, which control eye movement.
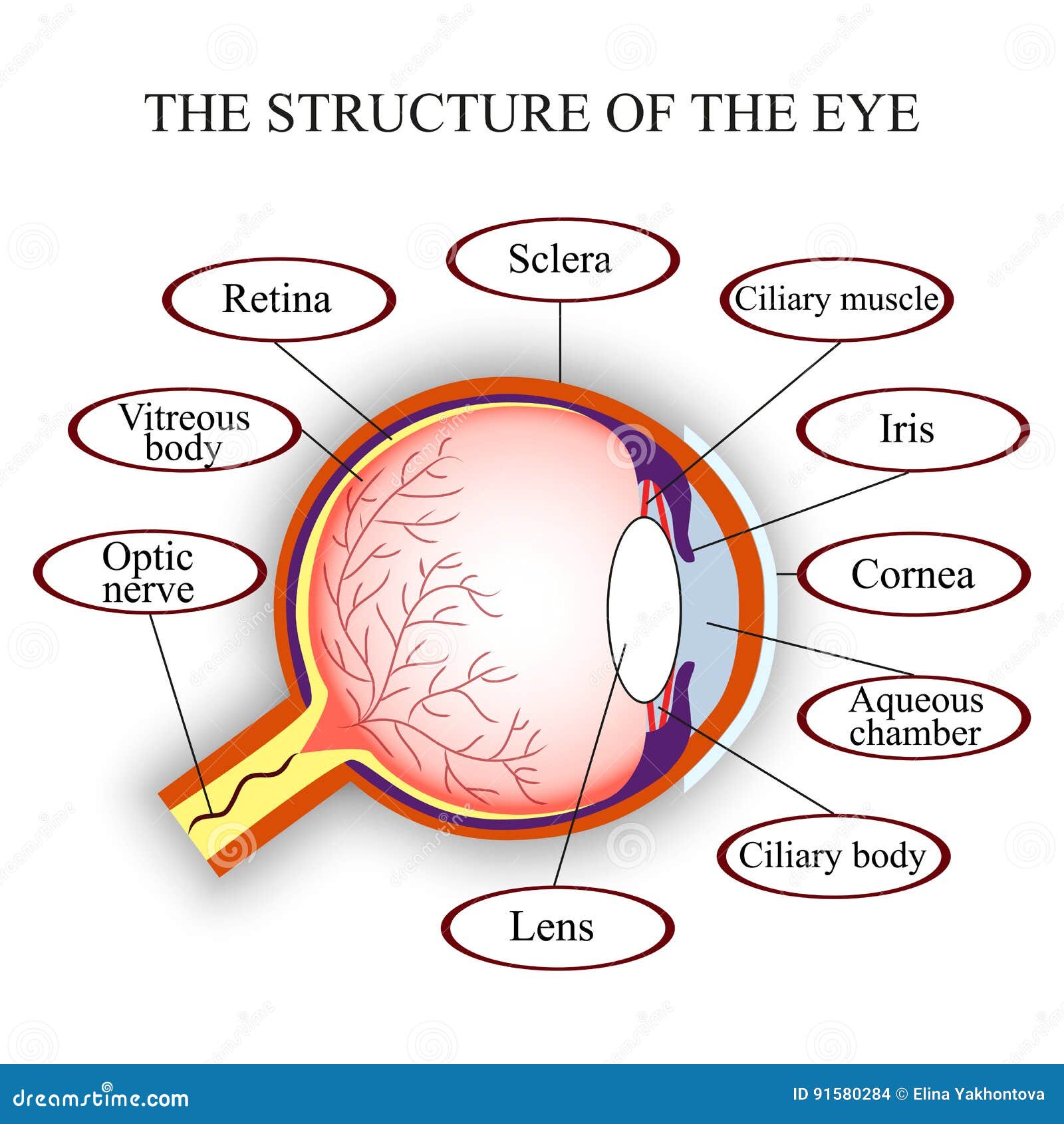
The mammalian eye is a sense organ that receives and coverts light of various wavelength reflected from object at varying distance, the visual field into electrical impulse which the optic nerves transmits to the brain where an image of remarkable precision is perceived

Structure And Functions of the different part of the Human Eye


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
